Introduction
In the competitive manufacturing landscape, project delays and budget overruns are among the most pressing concerns for managers, particularly in the fabrication of complex components like gears, where minute deviations can lead to assembly line failures. Traditionalgear manufacturing processoften rely on fragmented workflows and significant manual intervention, leading to inefficiencies and inconsistencies that challenge cost and quality control. This article demonstrates how integrating advanced CNC Machining technology with an optimized gear manufacturing process can establish a highly automated, data-driven production flow, fundamentally enhancing precision engineering capabilities. How can innovation in gear processing achieve this?
Why Have Traditional Gear Manufacturing Processes Become a Major Project Cost Risk?
Traditional gear creation methods, such as form cutting and basic hobbing, present significant limitations in modern manufacturing. These processes require extensive setup times and are heavily dependent on the skill and experience of machinists. This reliance on manual expertise introduces a high degree of variability, making it exceptionally difficult to maintain consistency across production batches .These limitations directly translate into substantial financial and project risks.
Protracted setup times and the scarcity of highly skilled technicians lead to inflexible production schedules and a diminished capacity to handle urgent orders. The inherent variability results in elevated scrap rates and frequent rework, which drives up unit costs and makes overall project expenses difficult to forecast accurately. Consequently, project timelines become unpredictable, and delivery commitments are often compromised, ultimately weakening an organization’s ability to deliver reliable Industrial Solutions . Studies by organizations like the American Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME) have highlighted that variability in manufacturing is a primary hidden factor eroding profitability and impacting customer satisfaction .
How Does Modern CNC Technology Revolutionize the Precision and Efficiency of Gear Machining?
Modern CNC Machining addresses the core shortcomings of traditional methods by utilizing digital programming to control machine tools with exceptional accuracy. This technology transforms complex gear geometries into repeatable machining paths. For instance, 5-axis machining centers can complete complex helical or bevel gears in a single setup, drastically reducing repositioning errors and shortening cycle times .
The revolution is further propelled by advanced gear cutting tools. Tools made from coated carbide or cubic boron nitride (CBN) offer superior hardness, thermal stability, and wear resistance. They enable higher cutting speeds and feed rates, boosting the efficiency of gear machining while ensuring longer tool life and more stable machining quality, thereby reducing the cost per part .
Most importantly, CNC technology elevates gear manufacturing to a realm of true Precision Engineering. Once a machining program is validated, it can be replicated infinitely, entirely eliminating the uncertainty introduced by human intervention. From blank to finished product, every tooth profile and lead is under strict programmable control, ensuring that every gear in a batch adheres precisely to design specifications.
Keep discovering with additional content crafted to inspire you.
What Core Competencies Should Be Prioritized When Selecting a Gear Machining Service?
Choosing a competent partner for custom gear machining is pivotal to project success. When evaluating a provider of manufacturing services, several core competencies should be scrutinized.
Technical Equipment and Process Control
Leading suppliers invest in state-of-the-art hardware and software. This includes high-precision CNC gear machining centers, gear inspection systems for full-parameter inspection, and the implementation of Statistical Process Control (SPC). SPC monitors key machining parameters in real-time to predict and prevent deviations, ensuring stability and consistency .
Material Science and Heat Treatment Expertise
A gear’s performance is largely determined by its material and subsequent heat treatment. An exemplary supplier possesses a rich material library and can provide expert selection advice based on application requirements, such as high load capacity, speed, or corrosion resistance. Crucially, they must have access to tightly controlled heat treatment processes to achieve the optimal balance between core toughness and surface hardness .
Industry Certifications and Quality Systems
Certifications are objective evidence of a supplier’s commitment and capability. For stringent industries, specific certifications are often mandatory:
- IATF 16949 Certification:
This global standard for automotive quality management systems demonstrates a supplier’s focus on defect prevention, reduction of variation, and continuous improvement, which is essential for automotive gear production. - AS9100D Certification:
This aerospace standard emphasizes product safety, reliability, and traceability. Selecting an AS9100D-certified supplier is fundamental for meeting the extreme reliability demands of the aerospace industry
For complex requirements, such as those in aerospace, a specialized CNC gear machining service provider can offer comprehensive solutions spanning design, material selection, processing, and inspection.
What Key Role Does Rapid Prototyping Play in the Gear Development Cycle?
In new product development, speed is critical. Rapid Prototyping significantly optimizes and accelerates the gear machining process from concept to validation.
Traditional methods for producing a functional gear prototype could take weeks. Today, technologies like metal 3D printing or quick CNC machining can produce functional gear samples within days. Metal 3D printing is suitable for innovative designs with complex internal features, while CNC machined prototypes use production-grade materials, offering mechanical properties close to the final part .
This capability allows design teams to conduct real rig tests, assembly checks, and load tests before investing in expensive production tooling. Rapid Prototyping helps identify potential issues like stress concentration, meshing interference, or noise vibration early in the design phase. This iterative process prevents costly design flaws from propagating into mass production, avoiding significant losses and project delays. Guidelines from engineering bodies like the German Association of Engineers (VDI) emphasize that rapid prototyping can reduce time-to-market by up to 30%, making it a crucial strategy for rapid market response .
H2: What Are the Indispensable Stages of a Successful Gear Project from Design to Mass Production?
A high-performance, reliable gear is the result of a meticulous, interconnected engineering process. A successful gear project typically encompasses the following indispensable stages, ensuring that the final product meets stringent specifications for precision, durability, and performance .
Front-End Engineering and Planning
This foundational stage sets the trajectory for the entire project. It begins with comprehensive design optimization, where engineers employ advanced CAD software to create detailed 3D models, focusing on Design for Manufacturability (DFM) to ensure the gear design is not only functional but also economically viable and producible . This phase includes determining critical dimensions such as tooth profile, pitch diameter, and pressure angle, often facilitated by precise calculations using tools like a helix gear calculator .
Following design finalization, scientific material selection takes place. Engineers choose materials based on operating conditions, required strength, wear resistance, and cost. Common selections range from carbon and alloy steels for high-strength applications to stainless steel for corrosion resistance, and non-ferrous materials like bronze or brass for specific operational needs . The chosen material must be suitable for the intended manufacturing and subsequent heat treatment processes .
Core Manufacturing and Modification
This stage transforms the digital design and raw material into a functional gear through a series of precise operations. It represents the heart of the gear cutting service.
- Gear Tooth Generation
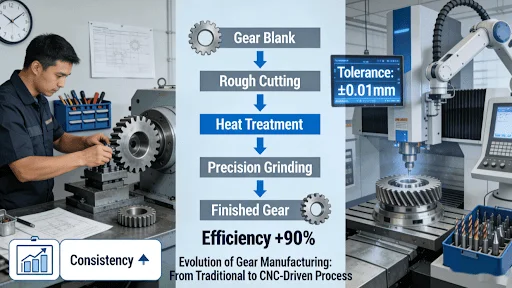
The initial phase involves creating the gear teeth on the prepared gear blank. Key methods include CNC gear hobbing, which is efficient for high-volume production of spur and helical gears; shaping for internal and complex external profiles; and broaching for internal teeth and keyways . Modern CNC technology ensures high precision and repeatability in these processes.
- Heat Treatment and Surface Modification
After tooth formation, gears undergo specialized heat treatment to enhance their mechanical properties. Processes like carburizing add carbon to the surface for a hard, wear-resistant exterior, while induction hardening uses electromagnetic fields to rapidly heat and harden the gear’s surface . This stage is crucial for achieving the desired balance of surface hardness and core toughness, significantly extending the gear’s service life .
Quality Assurance and Post-Processing
Quality assurance is integral throughout the entire workflow, culminating in rigorous final validation. Precision measurement starts with First Article Inspection (FAI) and continues with in-process checks. Advanced tools like Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) and gear measurement centers are used for comprehensive dimensional verification of tooth profile, pitch, and runout . Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, including X-ray and ultrasonic inspection, may be employed to detect internal defects without damaging the part .
Finally, surface treatments such as plating, coating, phosphating, or shot peening are applied. These enhance corrosion resistance, improve fatigue strength, and provide a final protective barrier . An excellent Manufacturing Services provider integrates all these stages to deliver end-to-end Industrial Solutions, acting as a trusted engineering partner capable of handling everything from design optimization to final finishing and quality certification .
Conclusion
In summary, adopting modern gear manufacturing process centered on CNC machining technology allows manufacturing enterprises to effectively mitigate the cost and quality risks associated with traditional methods. Integrating rapid prototyping into the development cycle and selecting a partner with comprehensive qualifications and capabilities are key to ensuring project success and enhancing market competitiveness.
Is your manufacturing project facing challenges with precision and cost? Immediately contact a precision manufacturing expert with international certifications such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and AS9100D to obtain a customized solution for your project.
Author Biography
This article contains technical insights from the precision manufacturing experts at JS Precision. With extensive experience in the field of precision component manufacturing, JS Precision is dedicated to providing global customers with high-quality Industrial Solutions through advanced processes including CNC machining, injection molding, and gear manufacturing.
FAQs
Q1: What are the most common materials used in gear machining?
Common materials include various steel alloys (e.g., 4140, 8620), stainless steel, cast iron, brass, and aluminum alloys. Material selection depends on the application’s requirements for strength, wear resistance, weight, and cost. High-precision gears are typically made from alloy steel and undergo heat treatment.
Q2: What are the typical tolerances achievable with CNC gear machining?
Tolerances depend on gear size and the specific machining process. For precision transmission gears, tooth profile tolerances can typically be controlled to ISO grades 6-8. Specific tolerances are determined by the gear module, diameter, and design requirements, and professional suppliers provide detailed technical consultation.
Can rapid prototyped gears be used in final products?
This depends on the prototyping technology. Metal 3D-printed prototypes can be used for functional testing, but their mechanical properties may differ from those of traditionally manufactured parts. CNC-machined prototypes, using the same materials, are closer to final production parts and can often be used directly for low-volume production or end-use.
What is the typical Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) for custom gear machining?
MOQ varies by supplier and gear complexity. Thanks to the flexibility of CNC machining, many professional service providers like JS Precision offer services ranging from single-piece prototypes to mass production, supporting on-demand orders to reduce inventory pressure.
How is quality and consistency ensured for custom gears?
A robust quality control system is essential. This includes First Article Inspection (FAI), in-process inspections (using equipment like gear measurement centers), and final inspection. Selecting a supplier certified to ISO 9001, IATF 16949, etc., is a fundamental guarantee.
Keep discovering with additional content crafted to inspire you at Management Works Media.