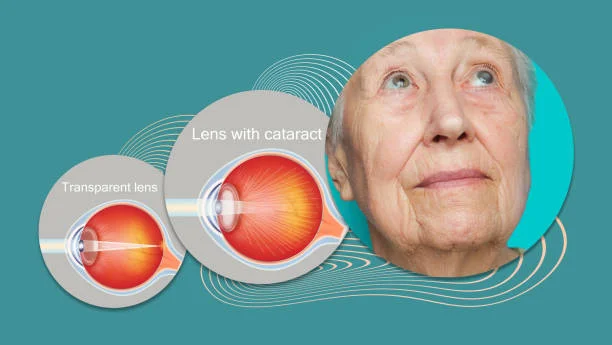
Cataract, commonly known as motiyabind in Bihar, is one of the leading causes of vision loss in India. It occurs when the natural lens of the eye becomes cloudy, gradually reducing clarity of sight. Generally cataract is age-related, people in Bihar often experience it earlier due to factors like prolonged sun exposure, working in fields or dusty environment, diabetes, and limited access to regular eye check-ups in rural regions.
Understanding the cataract symptomsat the right time is crucial because early recognition leads to a timely diagnosis and better treatment outcomes. Although cataract cannot be reversed with medicines or home remedies, keeping an eye on the progression is crucial until surgery becomes necessary. This blog explains the key symptoms of cataract, helping you recognise what changes in your vision may indicate motiyabind.
1. Blurred or Cloudy Vision
One of the earliest and most common symptoms of cataract is blurred or cloudy vision. People often describe it as looking through a foggy window or dirty glasses. In the initial stages, this blurriness may be mild and affect only a small part of your vision, but as the cataract grows, objects begin to appear increasingly hazy.
In Bihar, many individuals initially ignore this sign, assuming it is due to tiredness, pollution, or age-related weakness. However, if your vision does not improve even after cleaning your glasses or resting your eyes, it could be an early indication of cataract.
Don’t stop here—this related read unlocks a new perspective.
2. Increased Sensitivity to Light
Another common motiyabind symptom is a heightened sensitivity to light. Bright sunlight, vehicle headlights at night, or strong indoor lighting may start to feel uncomfortable or even painful. This is especially noticeable for people who travel frequently on Bihar’s roads during daytime or work outdoors.
This sensitivity happens because the clouded lens scatters light inside the eye instead of focusing it properly. If you find yourself frequently squinting or avoiding light, it may be time for an eye examination.
3. Difficulty Seeing at Night
Cataracts significantly affect night vision, making it challenging to see clearly in low-light conditions. People often report that they struggle while walking on poorly lit streets, climbing stairs in dim areas, or driving at night. The vision may appear dull, and details become harder to distinguish.
In rural and semi-urban areas of Bihar, where street lighting may be limited, this symptom becomes even more noticeable. Difficulty seeing at night is a strong sign of developing cataract.
4. Seeing Halos Around Lights
Many individuals with cataract start noticing halos or rings around lights, especially in the evening or at night. This happens because the cloudy lens causes light rays to scatter inside the eye, creating circular patterns around light sources.
This symptom is particularly troublesome for drivers who may find it hard to focus due to halo effects around vehicle headlights. If you frequently see halos, it may indicate the early onset of motiyabind.
5. Yellowing of Colours
Cataracts affect colour perception. Over time, colours may start to look faded, dull, or yellowish. For example, a bright red might appear brownish, or a vibrant blue might seem washed out.
This change happens gradually, so many people do not realise it immediately. It becomes noticeable only when comparing colours with others or after cataract surgery, when they realise how much brighter the world looks. If colours appear less vivid than before, it is likely due to cataract progression.
6. Double Vision
A unique symptom of cataract is double vision (diplopia) in one eye. Unlike typical double vision, which involves both eyes, cataract-related diplopia persists even if the other eye is closed.
This happens because the cloudy areas in the lens create multiple images. Initially, this may appear as slight overlapping or ghost images, but it can worsen as the cataract becomes denser. If you notice double vision from one eye, you should seek medical advice immediately.
7. Frequent Changes in Prescribed Glasses
People with cataract often need to update or change their glasses more frequently. Your reading power may suddenly increase, or you may find that your current glasses no longer provide clear vision.
Many people in Bihar assume that frequent power changes are just age-related, but if it happens repeatedly within a short period, it may signal early cataract. Eyeglasses might give temporary relief but cannot correct the clouding caused by the lens.
8. Reduced Contrast Sensitivity
Cataracts also affect the eye’s ability to perceive contrast, making it harder to differentiate between similar colours or objects against backgrounds of similar shades. Tasks like reading text on a low-contrast surface, distinguishing steps, or identifying objects in dim surroundings become challenging.
Reduced contrast sensitivity often goes unnoticed until daily activities begin to feel more difficult or risky, especially for elderly individuals.
9. Seeing Through a Yellow Tint
As cataract progresses, the lens often develops a yellow or brown tint, which influences the quality of vision. Everything may appear slightly tinted, affecting your ability to recognise colours accurately.
Many people initially mistake this for normal ageing, but persistent colour distortion is one of the defining cataract symptoms.
10. Vision That Fluctuates During the Day
Some individuals experience vision that changes throughout the day. It may be clearer in the morning and blurrier later, or vice versa. This fluctuation occurs because the lens absorbs fluid differently at different times, affecting its transparency.
If your vision changes frequently without any apparent reason, it may be linked to motiyabind.
11. Difficulty in Reading
Reading small text, whether on mobile screens, newspapers, or medicine labels, becomes difficult as cataract develops. You may notice that increased lighting does not solve the problem as effectively as before. This issue is particularly common among older adults and those who spend long hours reading.
Final Thoughts
Cataract is a gradual and painless condition, making it easy to overlook the early signs. However, recognising the symptoms of cataract—blurred vision, sensitivity to light, halos, poor night vision, colour changes, driving at night and frequent power shifts—can help in early diagnosis and timely treatment.
In Bihar, where motiyabind is one of the most common eye problems, regular eye check-ups are essential, especially for people above 40, diabetics, and those with prolonged sun exposure or family history. Cataract surgery is the only effective treatment and is safe, quick, and widely available. Eye drops or medicines cannot cure cataracts.
If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above, visit a qualified ophthalmologist immediately to protect your vision and quality of life.
Expand your knowledge with handpicked reads just for you at Management Works Media.